Hypersonic Wind Tunnel Research: Ray Tracing Inspires A New Approach
Forces and moments are fundamental quantities in physics, but in some circumstances—as in the case of models in hypersonic wind tunnels—they can be difficult to measure accurately. Taking a cue from the world of gaming, University of Maryland (UMD) associate professor Stuart Laurence has devised a means to obtain more precise results in such facilities. A faculty member in theaerospace engineering department, Laurence has now received a Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Young Faculty Award (YFA) that will provide $500,000 to support further development of this new approach.
Traditionally, researchers have measured the motion of free-flying bodies in wind tunnels by tracking individual markers on the body surface. Although forces and moments can be estimated indirectly through this means, the process is cumbersome and not very precise, Laurence said. Indeed, he said, the approach he is using yields levels of accuracy that are at least two orders of magnitude higher. Laurence credits the initial breakthrough to a former student, William Starshak, who began exploring whether techniques used by video game developers could be used to track free flying objects. Of particular interest: ray tracing, in which game developers track the behavior of light rays as they interact with an object, and are thus able to better recreate what the eye would see in a non-virtual environment. Now Laurence and his team have been able to extend the principle and devise a method that can be used for any number of scenarios involving one or multiple objects within a flow--for example, meteor fragmentation or the breakup of a satellite. “In any situation where you have an object of a known geometry moving freely, you could potentially use this approach to reconstruct the motion of that object,” Laurence said. The DARPA Young Faculty Award supports rising stars in junior research positions, providing generous funding and engaging selectees with the DARPA program development process. The long-term goal is to “develop the next generation of academic scientists, engineers, and mathematicians who will focus a significant portion of their careers on Department of Defense and National Security issues,” according to the agency’s website.
August 9, 2021 Prev Next |



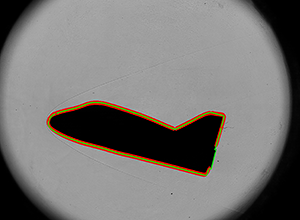 “We let models fly freely in the wind tunnel, with multiple cameras tracking them and creating silhouette images,” Laurence explained. “After the experiment, we run computer simulations to reproduce the recorded images based on estimates of the model position and orientation. By comparing the images to the simulations, we can determine how close the estimate is. We then iterate the process until we have a very accurate approximation to the model translation and rotation throughout the experiment.”
“We let models fly freely in the wind tunnel, with multiple cameras tracking them and creating silhouette images,” Laurence explained. “After the experiment, we run computer simulations to reproduce the recorded images based on estimates of the model position and orientation. By comparing the images to the simulations, we can determine how close the estimate is. We then iterate the process until we have a very accurate approximation to the model translation and rotation throughout the experiment.”